Definition of Research Data Management (RDM)
Research Data Management (RDM) is the care and maintenance required to (1) obtain high-quality data (whether produced or reused), (2) make the data available and usable in the long term (whether produced or reused) and (3) make research results reproducible beyond the research project (Biernacka et al., 2020; Bres et al., 2022; Research Data, n.d.; Voigt et al., 2022; Pauls et al., 2023; Bres et al., 2023). It complements research from planning to data reuse and deletion.
Relevance of RDM
Research data are valuable (Pauls et al., 2023) and therefore need to be managed systematically and responsibly (Biernacka et al., 2020). Incorporating robust RDM practices from the outset of a research project helps make research data accessible, reusable and verifiable throughout the research process and in the long term, regardless of the data producer (Pauls et al., 2023). Such practices also ensure integrity and help maximise the impact, reproducibility, transparency and rigour of researchers’ analyses and findings. Finally, robust RDM practices enhance collaboration and knowledge sharing and help preserve the scientific record and advance scientific knowledge.
Benefits and Drawbacks of RDM
As noted above, there are many benefits to incorporating robust RDM practices from the outset of a research project. For researchers, good RDM enhances visibility, reputation (by ensuring the quality of research), data ownership (i.e. “the possession of and responsibility for information” NCATS Toolkit) (Bres et al., 2022; Jacob et al., 2022) and helps them to meet formal requirements from third parties (e.g. research funders, institutions and publishers). For the project, good RDM brings clarity and findability, supports coordination, data security and good storage practices, helps to keep track of the project and deal with legal aspects, and increases eligibility for funding (Assmann et al., 2022; Bres et al., 2022; Bres et al., 2023). For the research group, good RDM enables knowledge management, transfer and preservation, while improving teamwork and saving time, money and resources (Assmann et al., 2022; Bobrov et al., 2021; Bres et al., 2022). For third parties, good RDM practices increase transparency, make data FAIR (i.e. findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable (no need for unnecessary duplication)) and increase collaboration (Assmann et al., 2022; Bobrov et al., 2021; Bres et al., 2022; Jacob et al., 2022; Voigt et al., 2022; Assmann et al., 2022). Last but not least, good RDM practices help to address societal challenges by ensuring reproducibility, availability and verifiability, preventing data loss and preserving the scientific record, ensuring good research practice (GRP) and supporting open science (i.e. open transfer of research knowledge, open access to research data) (Assmann et al., 2022; Bobrov et al., 2021; Engelhardt et al., 2022; Jacob et al., 2022; Lindstädt et al., 2019; Voigt et al., 2022; Bres et al., 2023).
There are also consequences of poor RDM practices, such as retractions of papers. For example, Dan Ariely, a professor of psychology and behavioural economics at Duke University, had one of his papers on dishonesty retracted. He could not remember in what year and in what form he had received the data from the company he was working with. Nor did he check the data for irregularities. The company could not find the data either (Bartlett, 2021). Another consequence might be that a paper, or in this case a book, has to be corrected and submitted again for review: Eliran Bar-El, a sociologist at the University of York had to correct his book “How Slavoj Became Žižek - The Digital Making of a Public Intellectual” because of “several insufficient, missing, or erroneous citations of source material upon which the author builds his argument” (Joelving, 2023).
Research Data Life Cycle
The research data life cycle is a model that illustrates the steps of RDM and describes how data should ideally flow through a research project to ensure successful data curation and preservation (Research Data Lifecycle, n.d.; Research Lifecycle Guide, 2024). It is intended to help researchers understand the scope and importance of data management (Sheikh et al., 2023). The research data life cycle can be illustrated as follow (RDMkit, 2021):
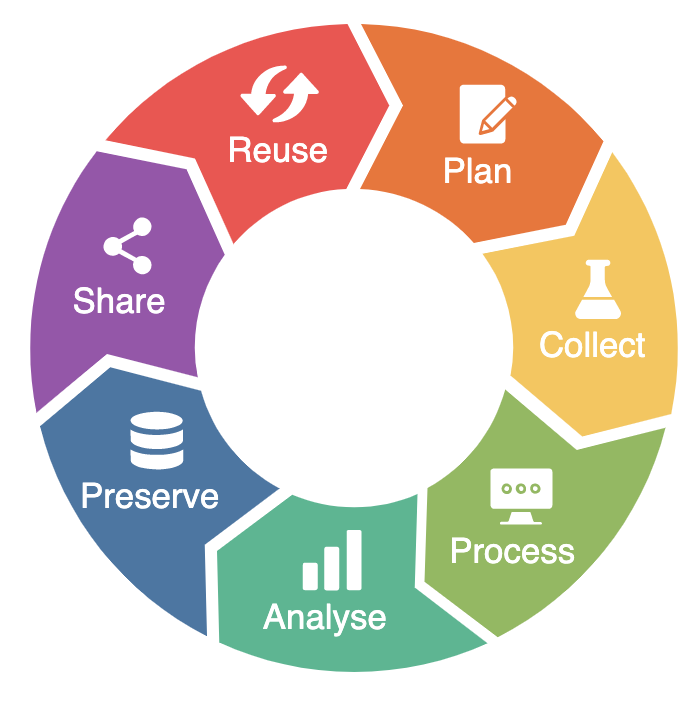
NFDI4Microbiota offers dedicated services and tools along the research data life cycle:
- Plan: a DMP template.
- Collect:
- Protocols on protocols.io.
- 2- to 3-hour workshops on ELNs (see example slides here).
- Training with eLabFTW (see example demo here).
- Annual seminar on ELNs.
- Process: metadata (standards):
- On this Knowledge Base.
- On GitHub.
- Analyse: the Cloud-based Workflow Manager (CloWM).
- Preserve: the ARUNA data orchestration engine, an open-source data management platform that allows scientists and industry partners to store, annotate and share their data according to the FAIR data principles.
- Reuse:
- StrainInfo, a service developed to provide a resolution of microbial strain identifiers by storing culture collection numbers, their relations, and culture-associated data.
- VirJenDB, a central hub connecting virus researchers to publicly available virus resources, metadata and sequences.
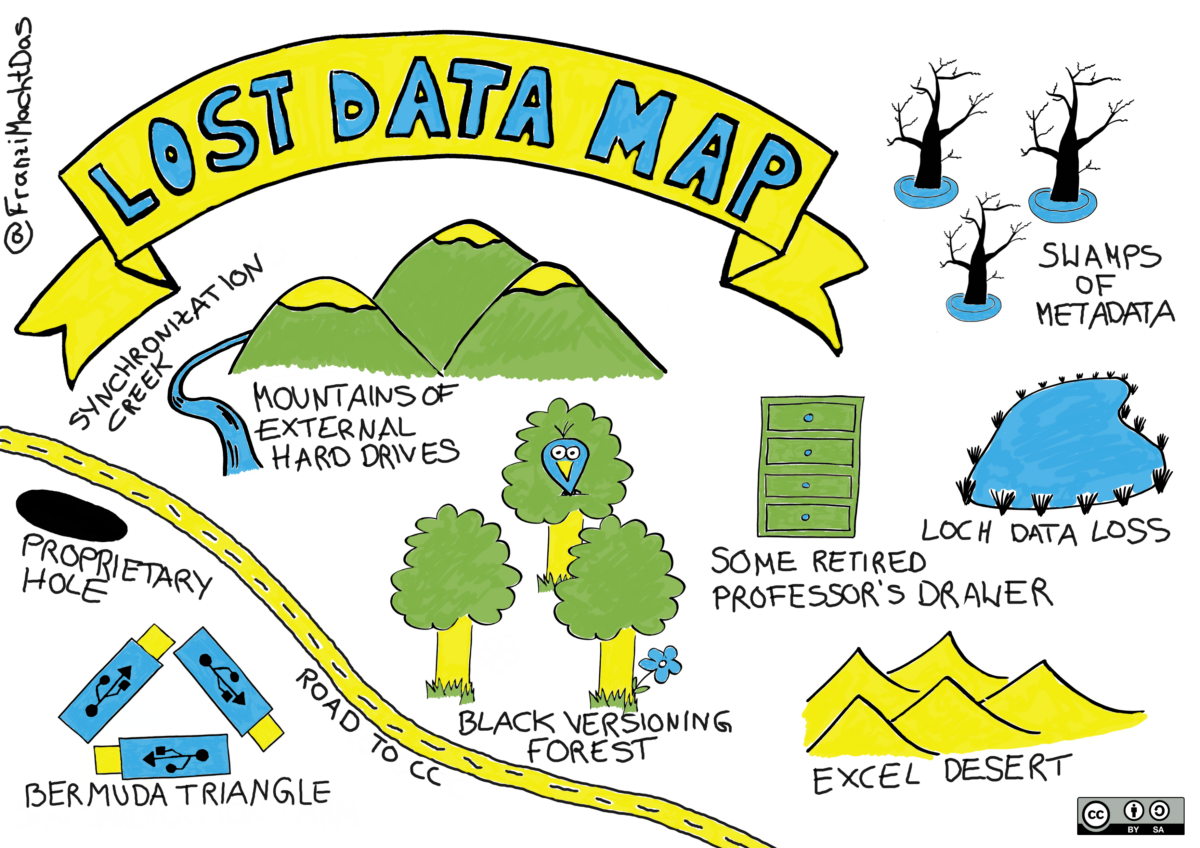
If the steps of the research data life cycle are not completed, data and results may be lost, or they may be preserved but without the necessary metadata to reuse them or make the research process reproducible (see Lost Data Map (Mau, 2019) below).
Measures of Good RDM
Below are measures of good RDM, grouped according to the steps in the research data life cycle. These measures are largely based on (Biernacka et al., 2020; Pauls et al., 2023; Steen et al., 2022), and some are explained in more detail on other pages of this Knowledge Base.
Plan
Planning a research project includes creating a research design, planning for data management (i.e. creating an initial DMP that outlines how data will be collected, processed and shared), exploring existing data sources and planning for consent to share data.
Collect
Even before the collection of research data, adopting an Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) may be a good measure to take. By digitising research notes, protocols and experimental results, an ELN can streamline data organisation and collaboration between team members. In addition, ELNs provide version control and real-time data capture, enabling seamless integration with RDM workflows. For example, researchers studying microbial communities could use an ELN to record observations, generate graphs and annotate results, all collaboratively, ensuring transparency and reproducibility. Collecting primary research data requires the creation of clear protocols for data collection, whereas collecting secondary data, i.e. the acquisition of existing third-party data, may require obtaining permission to reuse the data. Collecting research data also involves capturing data with metadata. For example, researchers studying bacterial evolution should carefully document their sampling procedures, including information on sampling sites, environmental conditions and sampling techniques to ensure reproducibility. Finally, collecting research data includes data validation (i.e. data cleaning and quality control), the use of acceptable file formats, and data check.
Process and Analyse
Processing research data begins with the proper documentation/description of the data. In terms of documenting scripts, code and software, software tools (from small analysis scripts to machine learning models) are integral to the processing, analysis and interpretation of complex microbiology data sets. Therefore, documenting the software environment, version numbers and dependencies used in data analysis workflows is critical to ensure reproducibility and transparency. For example, a study investigating the taxonomic composition of the gut microbiota may rely on custom Python scripts for data pre-processing and statistical analysis. By documenting these scripts, along with the parameters and input data used, researchers can enable others to replicate their analyses and validate their findings. In addition, the use of version control systems (VCS) such as Git, and the hosting of Git repositories on platforms such as GitHub or GitLab, ensures the traceability and accessibility of software artefacts. By incorporating such software management practices into their RDM strategy, microbiology researchers can improve the reproducibility, transparency and rigour of their computational analyses, thereby advancing scientific knowledge in the field. When it comes to documenting models, with the increasing use of machine learning in microbiology (e.g. to predict antibiotic resistance or classify microbial species), it is imperative that the underlying models are managed transparently. Researchers should document model architectures, training data and performance metrics to facilitate model validation and comparison across studies. Before research data can be analysed, it needs to be digitised, transcribed, translated and possibly anonymised. Clear protocols for data analysis must then be established. Finally, the data can be interpreted and research findings produced.
Preserve
Preserving research data requires establishing clear protocols for data storage and migrating data to appropriate media and formats. Adopting standardised formats, such as FASTA or the GenBank flat file format, facilitates interoperability and data sharing between studies, thereby enhancing collaboration and knowledge sharing with the microbiology research community. Data preservation also requires the creation of preservation documentation prior to the actual long-term preservation of data.
Share
Data sharing requires access control (i.e. selecting appropriate access to data) and data security. Researchers working with sensitive data, such as sensitive personal data (e.g. in clinical microbiology studies) or sensitive environmental data, need to consider protection and security measures to safeguard this information. Data sharing also requires that copyright be established before the data is actually shared and published. Microbiology researchers can embrace open-science practices by depositing their research data in public repositories such as NCBI’s GenBank or EMBL-EBI’s European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), thereby promoting transparency and long-term preservation of microbial data and ensuring its availability for future research.
Reuse
Reusing data includes reviewing results and previous research, conducting follow-up research, and using data for teaching and learning.
Issues and Challenges in RDM
Current issues and challenges in RDM can be classified by stakeholder, as individual researchers, research funders, research organisations, librarians and reviewers have different needs (Research Data Management, n.d.).
For individual researchers, the different organisational requirements can be confusing, especially if they work with different organisations, change their home institution or collaborate with researchers from other organisations where different rules apply (Research Data Management, n.d.; Sheikh et al., 2023). The lack of connectivity between tools used at different steps in the research data lifecycle can also be a barrier to the proper management of their data.
For research funders, the development of technological infrastructure can be difficult (Sheikh et al., 2023).
For research organisations, the institutional commitment and academic engagement required can be overwhelming. The lack of policy, funding and storage also hinders progress in RDM (Sheikh et al., 2023).
For librarians and RDM staff, raising awareness among researchers of the benefits of data sharing remains a challenge. On another note, librarians need (discipline-specific) skills and competencies to provide RDM-based services (Sheikh et al., 2023).
Developments and Initiatives in RDM
Internationally, the increasingly frequent requirement to produce a DMP has stimulated interest in RDM (Yamaji, 2024) and encouraged libraries to take an active role in RDM through advocacy, policy development, and advisory and consultancy services (Cox et al., 2017). Some institutions, such as KU Leuven, have also developed a dashboard to review datasets to meet funder requirements (Yamaji, 2024).
In Germany, the National Research Data Infrastructure (NFDI) funds nearly 30 discipline-specific consortia to help researchers make their data reusable in the long term.
Resources
General Resources
- Brief Guide - Research Data Management by Training Expert Group.
- The Research Data Management toolkit for Life Sciences RDMkit by ELIXIR
- Virtual Research Environment (VRE)
Platforms
- BExIS2 by NFDI4Biodiversity at FSU Jena
- Coscine by RWTH aachen
- GfBio consortium services
- Research Data Management Competence Base (RDM Compas) by KonsortSWD (social, behavioural, educational and economic sciences)
Bioinformatics and Life-science Resources
- Bio.tools: essential scientific and technical information on software tools, databases and services for bioinformatics and the life sciences.
-
G-Node infrastructure (GIN): GIN offers modern RDM for neuroscience. It is based on Gogs, git and git-annex technologies. GIN features include project management/coordination, large file support and data publishing. It also allows subfolders to be synchronised, shared and published independently of other subfolders. GIN also supports Markdown and LaTeX for manuscript writing. To use GIN, you must first create a new project repository and clone the research folder structure. You can then add a script that synchronises the repository and its submodules on double-click. You can also add submodules to a lab-wide repository.
- TMF-Portal ToolPool Gesundheitsforschung: The TMF-Portal was launched in 2017 and is operated by the Technologie- und Methodenplattform für die vernetzte medizinische Forschung e.V. (TMF). It provides a collection of IT infrastructure-related products for networked medical research. There are products from the TMF and from other providers such as companies and research institutions. There are over 80 products, more than half of which are software tools. Other product categories include eServices, reports and expert opinions, working materials and checklists, consultancy services and training courses. Products can be filtered by category, topic, project phase, keywords, provider and year. Similar products can also be compared using a feature matrix. On each product page you will find information about the use of the product in projects, testimonials from other users and references. New products can be submitted by anyone. Each product is then reviewed by a team of TMF members against a set of criteria before being added to the portal. To use the portal, follow this link. Many offerings are free and can be accessed directly from the portal. Software products usually require local installation and configuration (Steen et al., 2022).
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- SOP: Data management in clinical trials
- SOP: Data Management in the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
References
- Biernacka, K., Bierwirth, M., Buchholz, P., Dolzycka, D., Helbig, K., Neumann, J., Odebrecht, C., Wiljes, C., & Wuttke, U. (2020). Train-the-Trainer Concept on Research Data Management. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.4071471
- Bres, E., Rudolf, D., Lindstädt, B., & Shutsko, A. (2022). Research Data Management in Medical and Biomedical Sciences.
- Research Data. Retrieved June 6, 2023, from https://rfii.de/en/topics/#forschungsdaten
- Voigt, P., Frericks, S., Lindstädt, B., Shutsko, A., & Vandendorpe, J. (2022). Workshop on Research Data.
- Pauls, C., Feeken, C., Steen, E.-E., Lindstädt, B., Vandendorpe, J., & Markus, K. (2023). Workshop on Research Data Management.
- Bres, E., Rudolf, D., Lindstädt, B., Markus, K., Vandendorpe, J., & Riedel, R. (2023). Workshop on Research Data Management.
- Jacob, B., Kroehling, M. A., Mertzen, D., Straka, J., Lindstädt, B., Shutsko, A., & Vandendorpe, J. (2022). Workshop on Research Data.
- Assmann, C., Gadelha, L., Markus, K., & Vandendorpe, J. (2022). Workshop on Research Data Management.
- Bobrov, E., Adam, L.-S., Söring, S., Jäckel, D., Herwig, A., Lindstädt, B., Vandendorpe, J., & Shutsko, A. (2021). Workshop on Research Data.
- Assmann, C., Gadelha, L., Thölken, C., Lindstädt, B., Markus, K., Sutsko, A., Vandendorpe, J., & Hufsky, F. (2022). Research Data Management.
- Engelhardt, C., Biernacka, K., Coffey, A., Cornet, R., Danciu, A., Demchenko, Y., Downes, S., Erdmann, C., Garbuglia, F., Germer, K., Helbig, K., Hellström, M., Hettne, K., Hibbert, D., Jetten, M., Karimova, Y., Kryger Hansen, K., Kuusniemi, M. E., Letizia, V., … Zhou, B. (2022). D7.4 How to be FAIR with your data. A teaching and training handbook for higher education institutions. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.6674301
- Lindstädt, B., Vandendorpe, J., & von der Ropp, S. (2019). Research Data Management.
- Bartlett, T. (2021). A Dishonest Study on Dishonesty Puts a Prominent Researcher on the Hot Seat. https://archive.is/lHPsN
- Joelving, F. (2023). Publisher pulls books about philosophers Žižek and Venn over citation issues. https://retractionwatch.com/2023/11/13/publisher-pulls-books-about-philosophers-zizek-and-venn-over-citation-issues/
- Research data lifecycle. Retrieved June 6, 2023, from https://libguides.ntu.edu.sg/rdm/researchdatalifecycle
- Research Lifecycle Guide. (2024). Princeton Research Data Service. https://researchdata.princeton.edu/research-lifecycle-guide/research-lifecycle-guide
- Sheikh, A., Malik, A., & Adnan, R. (2023). Evolution of research data management in academic libraries: A review of the literature. Information Development. https://doi.org/10.1177/02666669231157405
- RDMkit. (2021). Data life cycle. ELIXIR. https://rdmkit.elixir-europe.org/data_life_cycle
- Mau, F. (2019). Sketchnote: Lost Data Map. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.4388672
- Steen, E.-E., Pauls, C., Feeken, C., Lindstädt, B., Shutsko, A., & Vandendorpe, J. (2022). Workshop on Research Data Management.
- Research Data Management. https://scienceeurope.org/our-priorities/open-science/research-data-management/
- Yamaji, K. (2024). Trends in Research Data Management. Indico.
- Cox, A. M., Kennan, M. A., Lyon, L., & Pinfield, S. (2017). Developments in research data management in academic libraries: Towards an understanding of research data service maturity. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68(9), 2182–2200. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.23781