Definition of research data
There is no consensus on the definition of research data as they are highly heterogeneous. Thus, the definition can vary considerably depending on the research funder, the scientific discipline or subject, and the research data itself (Lindstädt et al., 2019; Biernacka et al., 2020; Voigt et al., 2022). We propose the following definition, based on around 20 others: research data is the collection of digital and non-digital objects (excluding scientific publications) that are generated (e.g. through measurements, surveys, source work), studied and stored during or as a result of scientific research activities. These objects are commonly accepted in the scientific community as necessary for the production, validation and documentation of original research results. In the context of Research Data Management (RDM), research data also includes non-data objects such as software and simulations (see further examples below).
The characteristics of research data depend strongly on the context (i.e. conditions of generation, methods used, perspective) (Biernacka et al., 2020). Nevertheless, we can try to classify them as follows:
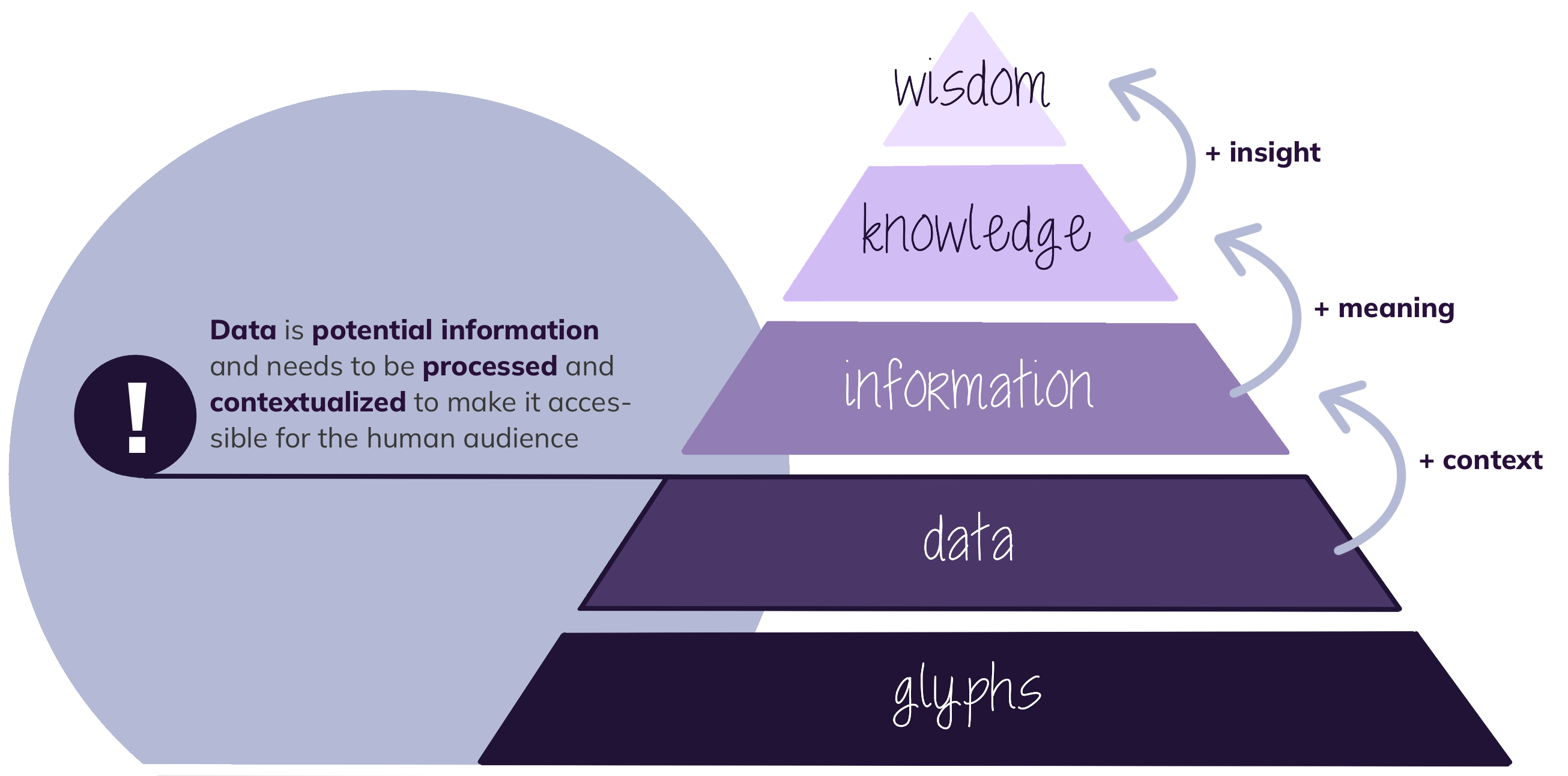
Primary or raw data is potential information generated by a researcher for the first time during a research project. It is unprocessed, possibly even untouched by human hands, unseen by human eyes, unthought by human minds. It needs to be contextualised to make it accessible to the human audience (Pomerantz, 2015; Darby, n.d.; Goldman & Martin, 2023). This data can be further categorised as observational (e.g. archaeological samples, brain scans, opinion polls), experimental (e.g. clinical trial data, DNA sequencing or organic material) and simulation, which is the modelling of complex processes (e.g. climate simulations) (Darby, n.d.).
Secondary data is data compiled from existing sources. This includes derived or compiled data (e.g. corpora, databases created by extracting information from multiple secondary sources) (missing reference).
Then there are processed data (i.e. raw data made useful (Goldman & Martin, 2023)), analysed data (i.e. processed data that has been interpreted (Goldman & Martin, 2023)), finalised, published or reference data (i.e. curated data that support your research question (Goldman & Martin, 2023), such as gene banks, national statistical archives (missing reference)) and information about the means necessary to generate data or replicate results (e.g. computer code, experimental methods) (missing reference).
Data is differentiated from information (i.e. processed data that can be consumed by humans), knowledge (i.e. information that has been assimilated by humans) and wisdom (i.e. applied knowledge) (Gerlich et al., 2023).
General data types
General data types include the following (Defining Research Data, n.d.; Steen et al., 2022; Voigt et al., 2022; DFG Guidelines on the Handling of Research Data, 2015):
- Data files (e.g. text files, binary files)
- Documents (e.g. word processing documents, spreadsheets)
- Measurement data, lab and observation data
- Lab and field notebooks, diaries
- Questionnaires, transcripts, codebooks
- Survey data
- Audio and video tapes
- Spectra
- Test answers
- Slides, artefacts, specimens, samples
- Database content (e.g. text, video, audio, images)
- Models, simulations, algorithms, scripts, code
- Content of an app (e.g. software) and research software
- Methodologies and workflows
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and protocols
Common data types in microbiology
Data types in microbiology include the following:
- Clinical data
- Crystallographic data
- Geospatial data
- Image data
- Linked genotype and phenotype data
- Linked Open Data (LOD)
- Macromolecular structures (e.g. electron microscopy data)
- Metabolomes
- Microbiome data (e.g. physical microbiome interactions)
- Nucleic acid sequences (e.g. raw sequencing data (reads or traces), amplicon, genome assemblies, annotated sequences) such as:
- DNA sequences
- (Meta)genomes
- Metagenome Assembled Genomes (MAGs)
- Genetic polymorphism
- Genomic features
- Genomic organisation
- RNA sequences
- 16S, 18S and ITS ribosomal RNA sequences
- Functional genomics / gene expression data (e.g. ribosome profiling, from microarrays)
- RNA-protein interactions
- Small RNA (sRNA)
- (Meta)transcriptomes
- Genetic variation data
- DNA sequences
- Protein sequences
- Protein-protein interactions
- (Meta)proteomes
- Quantitative and predictive food microbiology
- Sample and project (meta)data
- Scientific texts
- Semantic data
- Species interaction data (e.g. physical microbial interaction data)
- Standardised bacterial information
- Vertebrate-virus network
References
- Lindstädt, B., Vandendorpe, J., & von der Ropp, S. (2019). Research Data Management.
- Biernacka, K., Bierwirth, M., Buchholz, P., Dolzycka, D., Helbig, K., Neumann, J., Odebrecht, C., Wiljes, C., & Wuttke, U. (2020). Train-the-Trainer Concept on Research Data Management. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.4071471
- Voigt, P., Frericks, S., Lindstädt, B., Shutsko, A., & Vandendorpe, J. (2022). Workshop on Research Data.
- Pomerantz, J. (2015). Metadata. MIT Press.
- Darby, R. Research data defined. University of Reading Research Services. Retrieved July 10, 2021, from https://www.reading.ac.uk/research-services/research-data-management/about-research-data-management/research-data-defined
- Goldman, J., & Martin, E. (2023). Case Study. OSF. osf.io/qazrk
- Gerlich, S. C., Strupp, A., Hofmann, V., & Sandfeld, S. (2023). Training Course Material: Fundamentals of Scientific Metadata. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.10091708
- Defining Research Data. NC State University Libraries. Retrieved February 23, 2024, from https://www.lib.ncsu.edu/do/data-management/defining-research-data
- Steen, E.-E., Pauls, C., Feeken, C., Lindstädt, B., Shutsko, A., & Vandendorpe, J. (2022). Workshop on Research Data Management.
- DFG Guidelines on the Handling of Research Data. (2015). Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). https://www.dfg.de/resource/blob/172098/b08fcad16f1ff5ddca967f1ebde3a8c3/guidelines-research-data-data.pdf